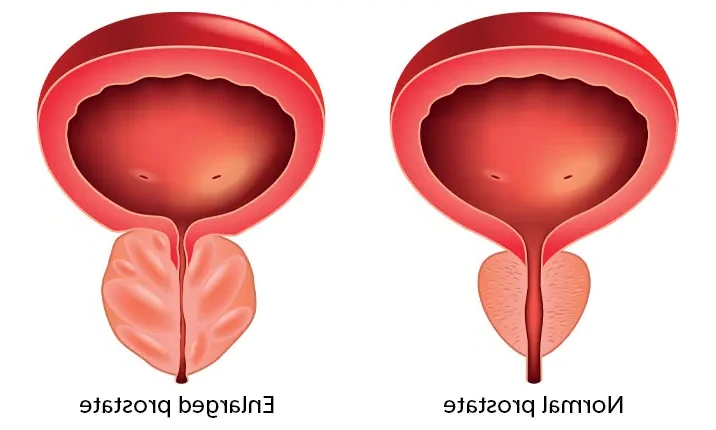
An increase in the size of the prostate gland causes prostate enlargement. This gland is situated at the base of the penis, beneath the bladder, and connects to the urethra. An enlarged prostate can cause irritation and difficulty urinating by interfering with the natural flow of urine. Prostate enlargement can result in more serious complications.
Estrogen
BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) is a common medical condition that affects older men. It helps to alleviate urinary tract symptoms and can have a significant impact on a man's quality of life. It affects 50 to 75 percent of men between the ages of 50 and 70. The hormones androgen and estrogen control prostate development. These hormone levels rise in men after they reach their twenties, when testosterone levels are at their peak. The ratio of estrogen to androgen in the bloodstream increases with age.
Estrogen has been shown to affect normal prostate gland function as well as promote pathological growth. Endogenous estrogens, which are produced by the gonads, and exogenous estrogens, which are produced by the prostate, are the two types of estrogens in circulation. The first of these, estrogen (E1), is produced from testosterone by an enzyme known as aromatase. This hormone, however, has only a minor impact on the estrogenic pathways in the prostate.

Genetics
While genetics play a role in the development of prostate enlargement, many other factors also play a role in the disease. Men who are African American or of African descent, for example, are more likely to develop the disease. African American men are also twice as likely as white men to die from the disease.
Prostate enlargement is a common problem that affects men in their forties and fifties. It's a condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and it causes a variety of urinary issues. The precise cause is unknown, but it is thought to be linked to genetics and time. It typically begins in men's early twenties and peaks around the age of 60, though some men develop symptoms as early as their forties. Men's prostates expand with age and can pinch off the urethra. An enlarged prostate can be painful and interfere with urination.
Time
Changes in hormone levels in the body as we age cause prostate enlargement. Benign prostatic hyperplasia refers to the enlargement of the prostate gland. Men experiencing symptoms of an enlarged prostate gland should seek medical attention to determine the best treatment options. An enlarged prostate gland can cause mild to severe symptoms. There is no need for immediate treatment in mild cases. Regular checkups and dietary changes can help alleviate symptoms.

While the symptoms of BPH may not be obvious at first, they are usually present when the condition is not treated. In severe cases, symptoms may include frequent and slowed urination, bladder function loss, and urinary tract infections. Men with BPH may develop incontinence in some cases.
Treatments
Men can choose from a number of prostate enlargement treatments. Some of these treatments are minimally invasive, with few to no side effects. Furthermore, these treatments have the potential to improve a patient's quality of life. However, not all treatments are effective for the condition. Prostate arterial embolization, for example, uses a radiofrequency device to target the enlarged prostate. The patient is then given medication to help relieve prostate pressure and open the urethra.
Surgical treatment is another option for prostate enlargement. This procedure, known as TURP, has been shown to be effective in the treatment of benign enlargement. There are, however, a number of risks associated with this treatment, and men with enlarged prostate glands should consult with their doctors before undergoing any surgery.


